Academic Projects
Ongoing Research
Predicition Model for Persistent Pain after Endometriosis Surgery
This project aims to develop a preoperative clinical model to predict pain-related outcomes after endometriosis surgery. The goal is to create a tool that can facilitate the decision-making discussion between patients and clinicians, thereby helping to personalize treatment for these patients. For this work, I am employing machine learning algorithms, including the exploration of neural networks, to model the complex relationship between preoperative factors in endometriosis patients and their pain outcomes. The model will be presented as an online calculator using the R Shiny platform and will be made available once this work is published. The project utilizes prospectively collected clinical data from the Endometriosis Pelvic Pain Interdisciplinary Cohort (EPPIC).
Original Clinical & Molecular Research
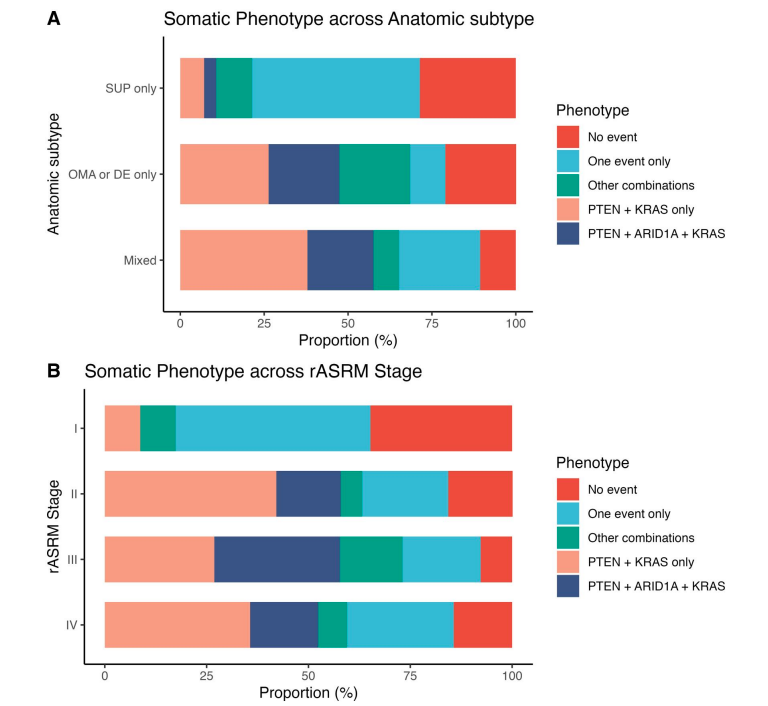
Somatic PTEN and ARID1A loss and endometriosis disease burden: a longitudinal study
Tucker DR, Lee AF, Orr NL, Alotaibi FT, Noga HL, Williams C, Allaire C, Bedaiwy MA, Huntsman DG, Köbel M, Anglesio MA, Yong PJ. Human Reproduction. 2024.
“Cancer-driver mutations have been identified in endometriosis cases without cancer, but their roles in the disease remain unclear. In this study, participants undergoing endometriosis surgery prospectively consented to have their tissue biopsy samples added to a biobank. I investigated the presence of abnormal alterations in two notable cancer-related markers: PTEN and ARID1A. Using immunohistochemistry, I assessed the pathology of the samples for loss of staining, indicative of potential loss or reduced presence of proteins associated with alterations or mutations in these genes. The analysis revealed that PTEN loss was common in endometriosis in this cohort (68%); it was also associated with worse anatomic severity, advanced disease stage, increased surgical difficulty, and ethnic disparities. These findings highlight the potential importance of PTEN loss and other somatic mutations in endometriosis as candidates for a future molecular classification system. All analyses (descriptive, bivariate, survival analyses etc.) and visualizations were conducted using R.
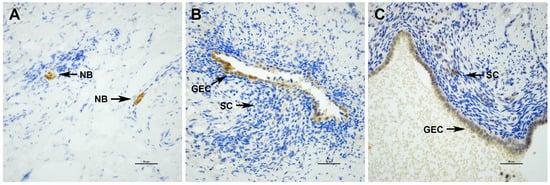
Nerve Bundle Density and Expression of NGF and IL-1β Are Intra-Individually Heterogenous in Subtypes of Endometriosis
Sreya M, Tucker DR, Yi J, Alotaibi FT, Lee AF, Noga H, Yong, PJ. Biomolecules. 2024;14(5):583.
Endometriosis is a gynecological disorder marked by local inflammation and increased nerve bundle density due to elevated nerve growth factor (NGF) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) levels. We analyzed tissue samples from 12 patients with various endometriosis subtypes (deep, superficial peritoneal, endometrioma), using immunohistochemistry to measure nerve bundle density (PGP9.5) and NGF and IL-1β expression. Our findings revealed significant heterogeneity in nerve bundle density and marker expression across different lesion subtypes within the same patient, with most patients showing a coefficient of variation (CV) ≥ 100%. These results suggest that future studies should stratify markers of neuroproliferation by anatomic subtype to improve clinical correlations.
Pelvic pain comorbidities and quality of life after endometriosis surgery
Tucker DR, Noga HL, Lee C, Chiu DS, Bedaiwy MA, Williams C, Allaire C, Talhouk A, Yong PJ. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2023;229(2):147.e1-147.e20.
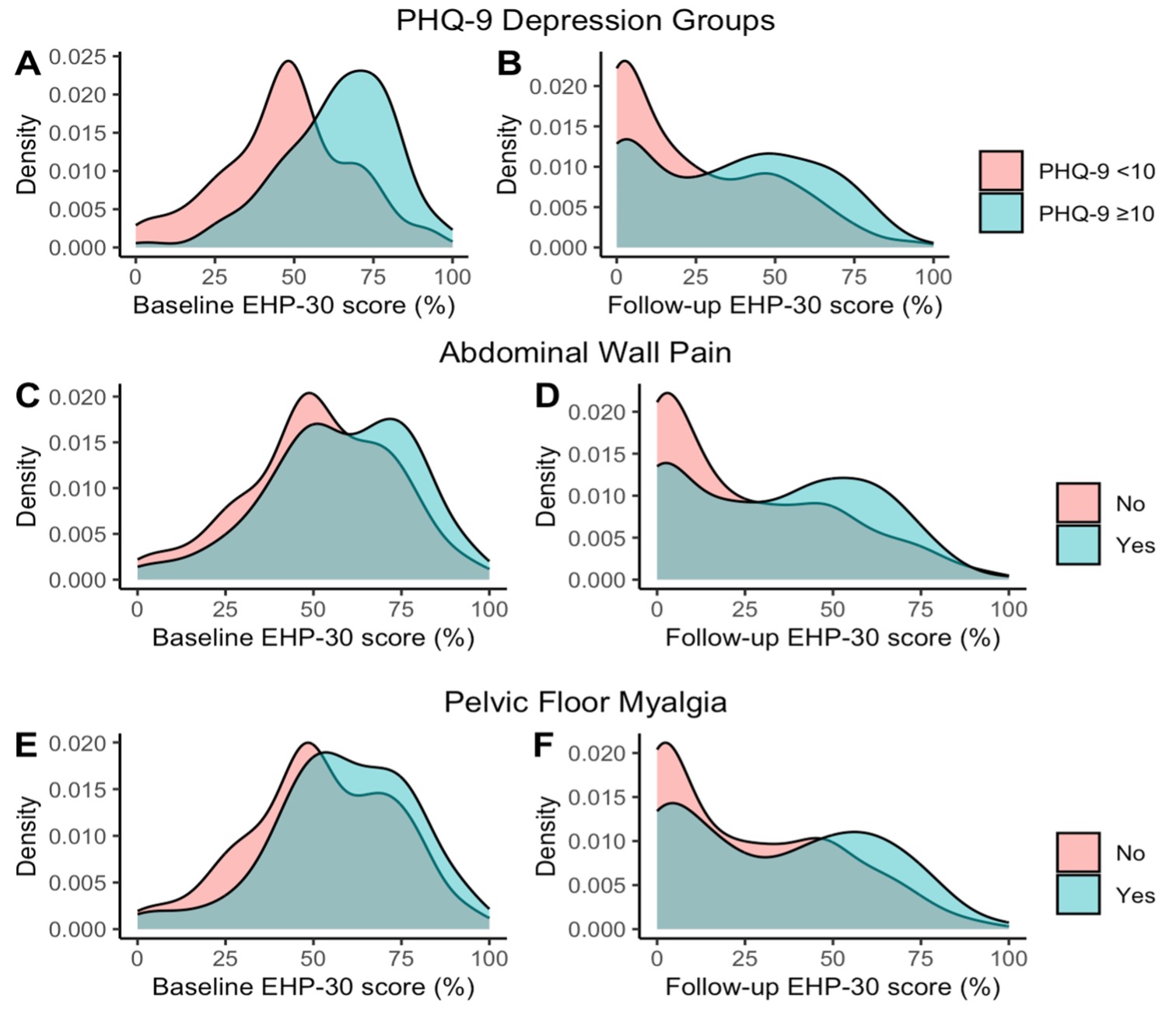
Endometriosis is a chronic condition affecting ~10% of reproductive-aged women. Surgery is an effective treatment for most individuals with endometriosis-related pain, however a significant proportion experience persistent/ recurrent pain. Persistent/ recurrent pain after endometriosis surgery may be due to central sensitization or nociplastic pain. In centralized pain, pain processing in the brain is altered leading to pain perception even after the pain stimili (e.g. endometriosis lesions) is removed. In this prospective longitudinal study, we used multivariable linear regression models to examine whether the preoperative presence of pelvic pain comorbidities, indicative of underlying central sensitization,is associated with worse pain-related quality of life after endometriosis surgery. Additionally, we trained LASSO regression models via cross-validation to identify the most influential variables on follow-up quality of life scores and presented coefficients and confidence intervals based on 1000 bootstrap samples.
Standardized protocol for quantification of nerve bundle density as a biomarker for endometriosis
Zoet G, Tucker DR, Orr NL, Alotaibi FT, Liu YD, Noga H, Köbel M, Yong PJ.Front Reprod Health. 2023;5:1297986.
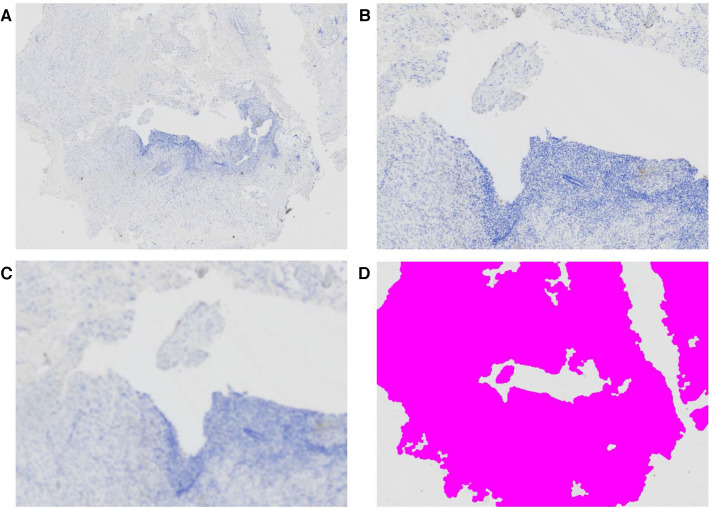
We propose a standardized protocol for the measurement of nerve bundle density (PGP9.5) in endometriosis environment (including deep endometriosis, ovarian endometriomas and superficial peritoneal endometriosis) as a potential biomarker reflecting local neurogenesis.
Journal Reviews
Scoping review of biosimilar disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in pregnancy: evidence gaps and proposed outcome reporting framework
Cheng V, Amiri N, Cheng V, Ellis U, Cragg JJ, Proulx L, Tucker DR, & De VeraMA. Rheumatology international.2025
This scoping review examined what is currently known about the use of biosimilar biologic drugs—lower-cost versions of biologic therapies during pregnancy. We identified only six small studies, mostly descriptive, involving biosimilars used to treat autoimmune conditions such as arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease. Reported outcomes varied and were inconsistently measured, highlighting major evidence gaps. To improve future research, we proposed a Reproductive Health Outcomes Reporting Framework. Our review is the first synthesis of perinatal evidence on biosimilar DMARDs and underscores the need for larger, standardized studies to guide safe treatment during pregnancy.
Assessing the Utility of artificial intelligence in endometriosis: Promises and pitfalls
Dungate B, Tucker DR, Goodwin E, Yong PJ. Womens Health (Lond). 2024;20:17455057241248121.
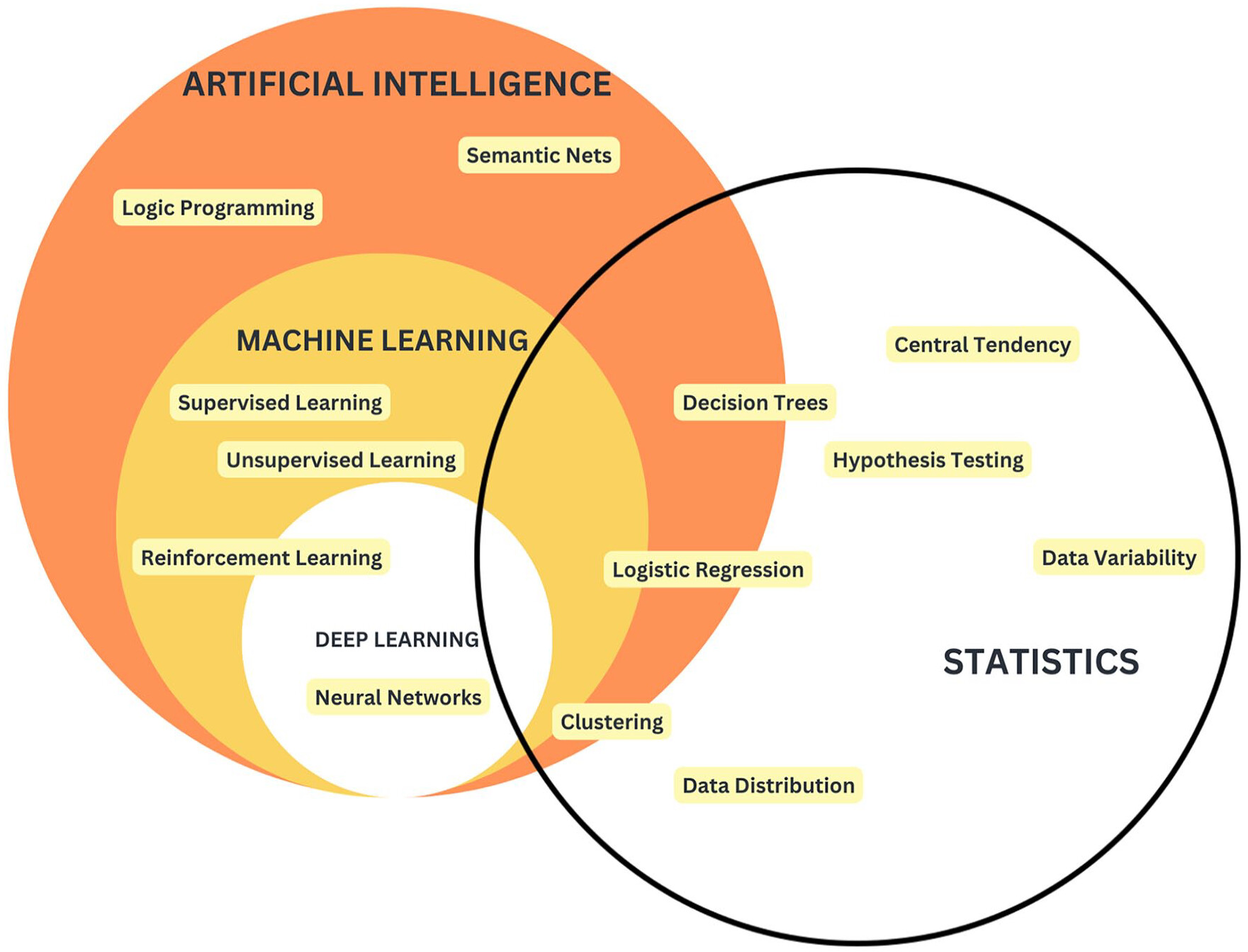
This study examines how artificial intelligence (AI) can improve the diagnosis and treatment of endometriosis, a condition that affects many women but is underfunded and hard to diagnose due to varied symptoms. AI, which analyzes large datasets to find new patterns, is increasingly used in medical research. Its applications in endometriosis include diagnostic tools and treatment prediction, potentially reducing diagnostic delays, healthcare costs, and providing better treatment options. However, AI’s success depends on high-quality data and skilled implementation. The review highlights the need for careful and transparent use of AI to avoid mistakes and ensure reliable outcomes, calling for more oversight in AI research to enhance endometriosis care.
Circular RNA and its potential as prostate cancer biomarkers
Tucker D, Zheng W, Zhang DH, Dong X. World J Clin Oncol. 2020;11(8):563-572.
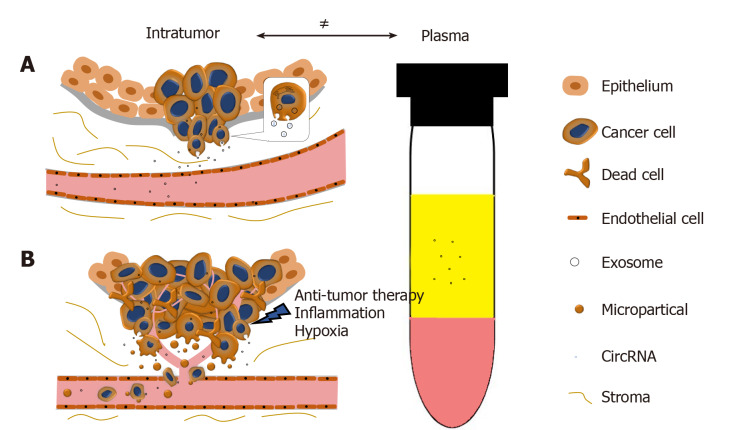
Advancing knowledge of the transcriptome has revealed that circular RNAs (circRNAs) are widely expressed and evolutionarily conserved molecules that may serve relevant biological roles. More interesting is the accumulating evidence which demonstrates the implication of circRNAs in diseases, especially cancers. This revelation has helped to form the rationale for many studies exploring their utility as clinical biomarkers. CircRNAs are highly stable due to their unique structures, exhibit some tissue specificity, and are enriched in exosomes, which facilitate their detection in a range of body fluids. These properties make circRNAs ideal candidates for biomarker development in many diseases. This review will outline the discovery, biogenesis, and proposed functions of circRNAs.